Unlocking the Potential of GenAI in ADMS: A Way to Successful Implementation
A comprehensive framework for GenAI adoption, from strategy to execution

Generative AI (GenAI) is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a transformative force that is revolutionizing IT organizations and transforming the world of software development. With its immense potential to streamline operations, GenAI can be applied across various domains around the world. Software development often requires extended time to complete the project/product and deliver without defects, making it a complex process to manage within tight deadlines. GenAI offers organizations the ability to streamline development, testing, and delivery, making it ideal for ADMS implementation.
Today, businesses of all sizes are actively exploring the integration of GenAI into their day-to-day operations. However, successful adoption begins with assessing organizational readiness, identifying the key challenges, and establishing clear validation criteria. This is where a GenAI Readiness Checklist (GAIRC) comes in, a tool to help GenAI into the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) and beyond, particularly in maintenance.
Let’s examine the categories to verify an organization’s preparedness for integrating GenAI in their IT field using GAIRC:
- Organization Responsibility
- Third-Party Responsibility
- Tools And Techniques Availability
- Resources Availability
- Security Concerns
These requirements align with several key parameters, as shown below:
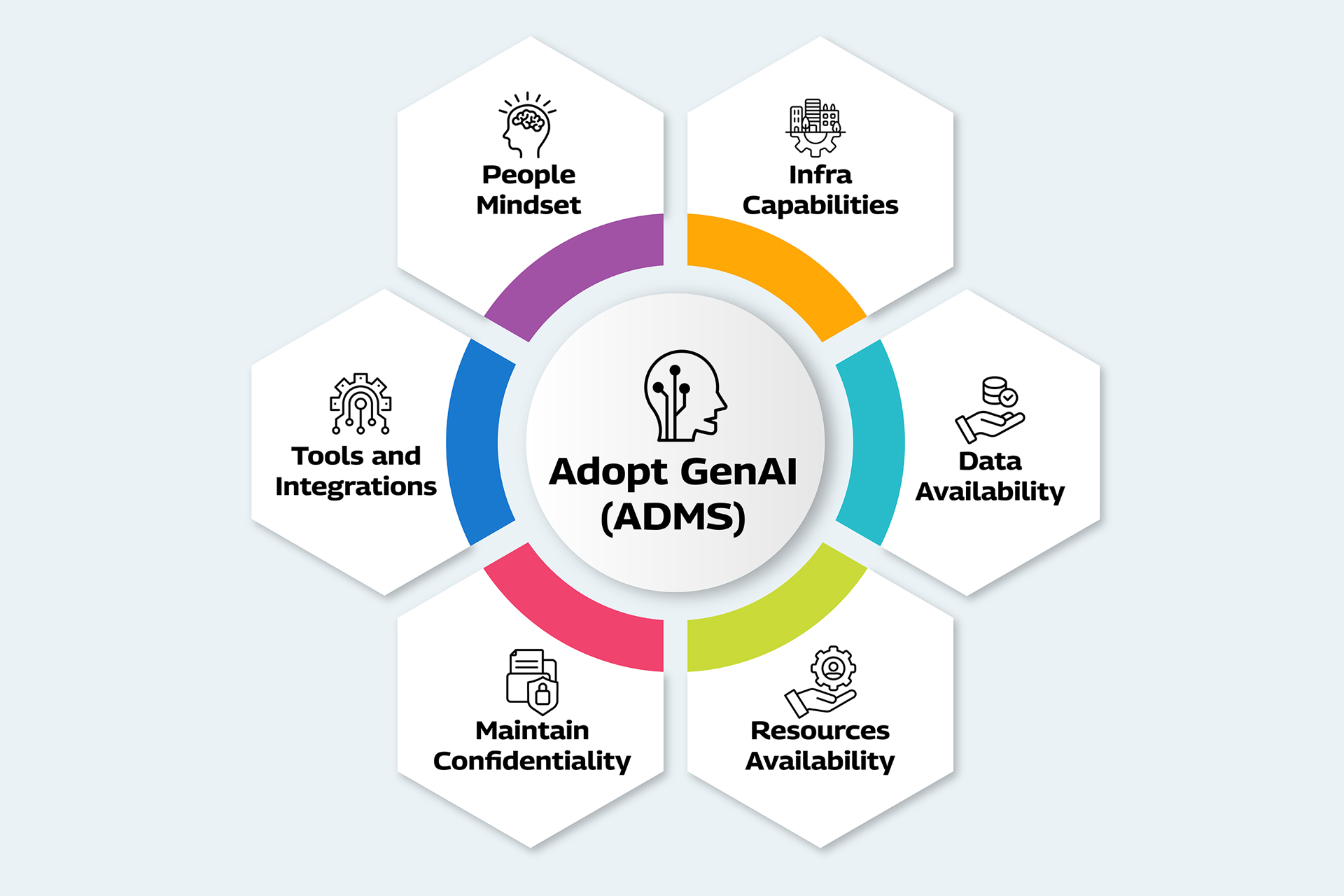
Key Parameters for GenAI Readiness
- Infrastructure Capabilities: The organization must possess adequate infrastructure to define DevOps, and Quality Engineering (QE) environments with hardware, software, and data systems including GenAI training.
- Data Availability: In today’s data-driven world, GenAI models require high-quality, comprehensive data to learn and generate outcomes. This data often comes from log files generated by various systems, servers, and historical data for predictive maintenance within ADMS.
- Resources: Physical resources, such as a skilled development team, are essential to identify, define scope, and implement appropriate use cases for Development, Maintenance, and QE, including application maintenance within ADMS.
- Confidentiality: To ensure data confidentiality and security, organizations must enforce strict security protocols for storing sensitive data within their internal systems used in ADMS.
- Tools: When implementing AI algorithms, they should use commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) and open-source tools and explore third-party algorithms that are not limited to the tools required for ADMS implementation.
- Mindset: A culture that embraces innovation and continuous improvement is crucial. Organizations should recruit individuals who are passionate about AI/GenAI implementation within ADMS.
- Integrations: Effective communication and integration between internal, external, and cloud infrastructure systems are crucial to understanding and implementing potential use cases for GenAI/AI within ADMS.
Implementation of GenAI in ADMS
Below are the key steps to implement GenAI in organizations:
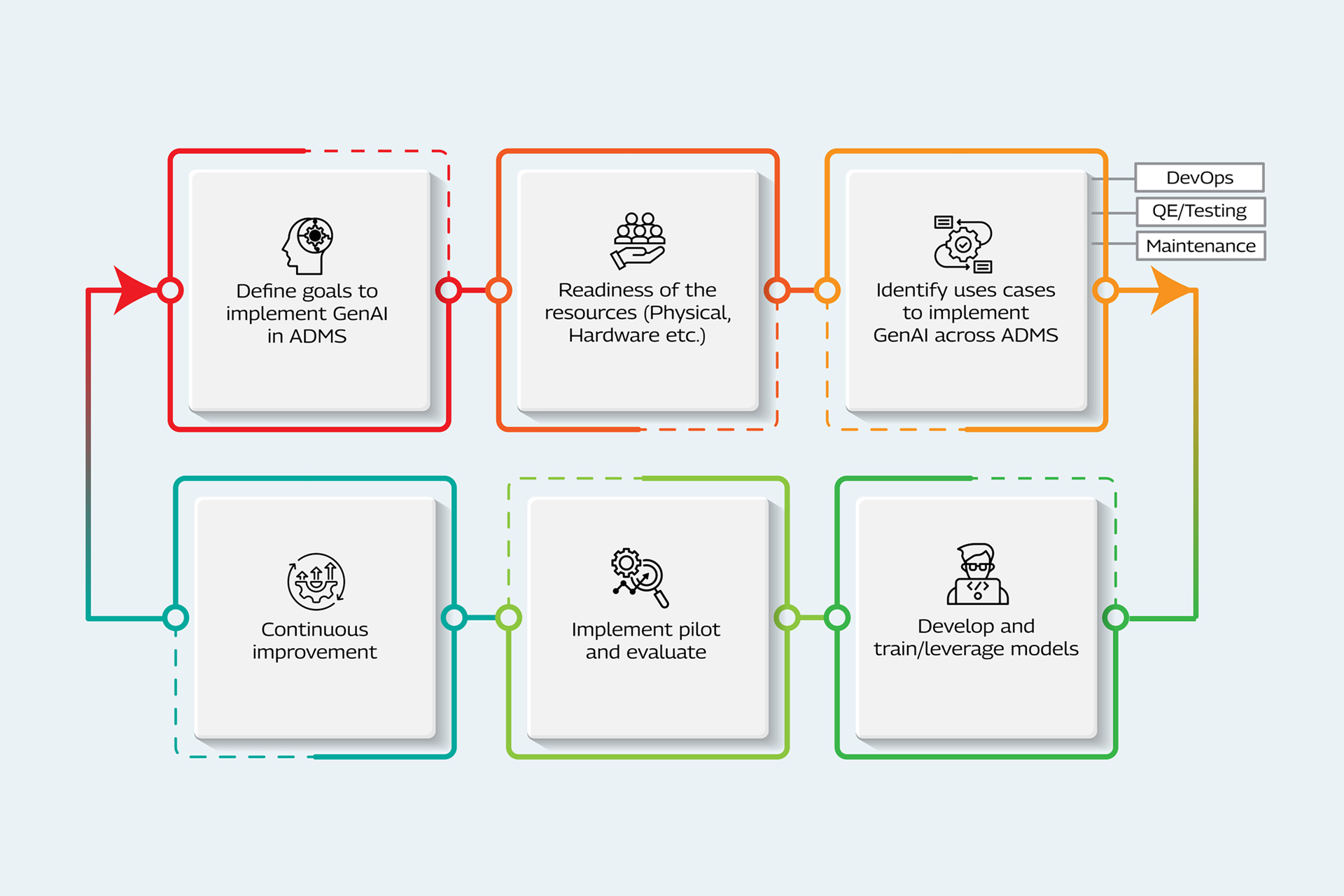
- Define Goals to Implement GenAI in ADMS
Align the goals of GenAI implementation within the broader ADMS (Development, QE, and Maintenance) objectives and strategic vision. Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure their impact and relevance. Prepare a detailed action plan for the upcoming months or quarters, setting key milestones. Highlight benefits such as increased efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced product quality—that GenAI will deliver. - Readiness of The Resources
Ensure the organization has the necessary resources including skilled personnel, hardware, and software infrastructure to support GenAI initiatives. Additionally, ensure the availability of relevant data for training models specifically for organizational use cases within ADMS. - Identify Use Cases to Implement GenAI across ADMS
Prepare a list of use cases covering Development, QE, and Maintenance that could significantly impact the organization’s business. Evaluate the feasibility of implementing GenAI for each use case and prioritize them. The identified use cases should be specific to the organization, domain, and IT-oriented (DevOps, QE, etc.). - Develop and Train Large Language Models (LLMs)
As per the organization's requirement, identify suitable Large Language Models (LLMs) to address the use cases. Identify the suitable data (synthetic/historical) in volumes training and testing on the identified model. Based on the feedback, fine-tune the model till it meets the desired performance levels. - Implement Pilot and Evaluate
Define a phased approach to adopt GenAI in the organization, starting with a proof-of-concept (POC), followed by a pilot phase and execution. Demonstrate the outcome, and key findings including the performance also plan for the next steps to fine-tune and adopt GenAI. - Continuous Improvement
Feedback is essential to refine and improve the performance of the model and the response to address use cases defined in ADMS. Implement the feedback to scale the solution to adopt at the organization level.
Review Checklist: Parameters for GenAI Implementation*
- The current data maturity level of the organization must be assessed to ensure readiness for GenAI adoption.
- The identified ADMS and business objectives should be clearly defined to align GenAI implementation to meet the overall organizational goals.
- The state of digital transformation plays a crucial role.
- It is important to evaluate whether the organization has sufficient data science and AI expertise or not.
- Processes and tools for managing intellectual property should be in place to protect valuable assets during implementation.
- The organization must have a skilled workforce capable of leveraging GenAI technology.
- KPIs should be established to measure data usage and assess the success of GenAI deployment.
- Robust data privacy and security capabilities are essential for safeguarding sensitive information.
- The support from third-party vendors must be adequate for GenAI solutions.
Conclusion
The adoption of GenAI in organizations, particularly in ADMS, accelerates innovation and enhances the quality of the outcome by increasing efficiency and time to market. The successful implementation requires a comprehensive readiness assessment, like the GAIRC, ensuring the readiness across infrastructure, data availability, resources, confidentiality, tools, mindset, and integrations.

Kishore Kandula is a technology leader with 22+ years of experience in testing, test automation, DevOps, and AI/GenAI in the software service industry. He has worked across multiple sectors including banking, oil and gas, and manufacturing, managing large teams with expertise in test automation, RPA, DevOps, and Agile initiatives.More
Kishore Kandula is a technology leader with 22+ years of experience in testing, test automation, DevOps, and AI/GenAI in the software service industry. He has worked across multiple sectors including banking, oil and gas, and manufacturing, managing large teams with expertise in test automation, RPA, DevOps, and Agile initiatives. He frequently participates in customer workshops, providing the right tools, framework, and the required approach to generate early ROI. Kishore has established expertise in setting up end-to-end automation from design to execution using different tools, including licensed and open source. He is also certified in test automation, RPA, machine learning, blockchain, and metaverse.
Less







